PubMed
Astrocytes mediate the effect of oxytocin in the central amygdala ...
Oxytocin (OT) orchestrates social and emotional behaviors through modulation of neural circuits. In the central amygdala, the release of OT modulates inhibitory circuits and, thereby, suppresses fear responses and decreases anxiety levels. Using astrocyte-specific gain and loss of function ...
Nature
Brain oxytocin: how puzzle stones from animal studies translate ...
The neuropeptide oxytocin has attracted great attention of the general public, basic neuroscience researchers, psychologists, and psychiatrists due to its profound pro-social, anxiolytic, and “anti-stress” behavioral and physiological effects, and its potential application for treatment ...
PubMed
Oxytocin injected into the ventral subiculum or the posteromedial ...
Oxytocin (20-100 ng) was found to be able to induce penile erection when injected unilaterally into the ventral subiculum or the posteromedial cortical nucleus of the amygdala of male rats. The pro-erectile effect started mostly 30 min after treatment and was abolished by the prior injection ...
ScienceDirect

Oxytocin in the medial prefrontal cortex attenuates anxiety: ...
However, questions remain about ... OT and its mechanism of action. Here we assessed whether the regulation of anxiety by mPFC OT is restricted to the PL subregion and evaluated whether oxytocin receptor (OTR) activation is required for OT to have an anxiolytic effect. We also examined whether OT interacts with GABA in the mPFC to reduce anxiety and investigated the extent to which OT in the mPFC affects activation of mPFC GABA neurons as well as neuronal activation in the amygdala, a primary ...
Nih
Nonsocial Functions of Hypothalamic Oxytocin - PMC
Oxytocin (OXT) is a hypothalamic neuropeptide composed of nine amino acids. The functions of OXT cover a variety of social and nonsocial activity/behaviors. Therapeutic effects of OXT on aberrant social behaviors are attracting more attention, such ...
Nih
Neurophysiological effects of acute oxytocin administration: ...
Oxytocin (OXT) plays a prominent role in social cognition and may have clinical applications for disorders such as autism, schizophrenia and social anxiety. The neural basis of its mechanism of action remains unclear. We conducted a systematic ...
Psychiatryonline
Oxytocin and Behavior: Evidence for Effects in the Brain | The ...
This installment of the Windows to the Brain series offers an overview of oxytocin's many and varied effects, sites of action in the brain, and stimuli that are implicated in its actions. These include response to infant behavior, such as laughing or crying, “falling in love,” and abandonment.
NCBI
Intranasal Oxytocin Affects Amygdala Functional Connectivity after ...
Approximately 10% of trauma-exposed individuals go on to develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Neural emotion regulation may be etiologically involved in PTSD development. Oxytocin administration early post-trauma may be a promising avenue ...
MDPI
The Role of Oxytocin in Abnormal Brain Development: Effect on Glial ...
Moreover, we cover the most up-to-date ... effects it holds when adverse neural events arise in association with neuroinflammation. A detailed assessment of the underlying mechanisms between OT treatment and astrocyte and microglia reactivity is given, as well as a focus on the amygdala, a brain region of crucial importance for socio-emotional behavior, particularly in infants born preterm. Keywords: oxytocin; developing ...
OUP Academic
Oxytocin Affects the Connectivity of the Precuneus and the Amygdala: ...
January 22, 2015 - An improved understanding of the neurophysiological effects of oxytocin can be important in terms of evaluating the mechanisms that are likely to underlie the clinical responses observed upon long-term oxytocin administration. oxytocin, resting-state, amygdala, precuneus, fMRI · Oxytocin (OXT) is one of the most widely studied neuropeptides in recent times, mainly because of its ...
PubMed
The analgesic effects of oxytocin in the peripheral and central ...
Pain is a ubiquitously unpleasant feeling among humans as well as many animal species often caused by actual and potential tissue damage. However, it is absolutely crucial for our survival in many ways. Acute pain can signal the presence of danger or life-threatenting events, which help escape ...
NCBI
Oxytocin signaling in basolateral and central amygdala nuclei ...
The present study investigated how oxytocin (OT) signaling in the central (CeA) and basolateral (BLA) amygdala affects acquisition, expression, and extinction of context-conditioned fear (freezing) in rats. In the first set of experiments, acquisition ...
NCBI
Therapeutic uses of oxytocin in stress-related neuropsychiatric ...
Oxytocin (OXT), produced and secreted in the paraventricular nucleus and supraoptic nucleus of magnocellular and parvocellular neurons. The diverse presence and activity of oxytocin suggests a potential for this neuropeptide in the pathogenesis and treatment ...
Nature
Oxytocin induces long-lasting adaptations within amygdala circuitry ...
Intranasal administration of the neuropeptide oxytocin (IN-OT) is increasingly explored as a potential treatment for targeting the core symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). To date, however, the impact of multiple-dose IN-OT treatment on human neural circuitry is largely unknown, and ...
Nature
Oxytocin modulates social value representations in the amygdala ...
Humans exhibit considerable variation in how they value their own interest relative to the interests of others. Deciphering the neural codes representing potential rewards for self and others is crucial for understanding social decision-making. Here we integrate computational modeling with ...
Nih
Roles of Oxytocin in Stress Responses, Allostasis and Resilience - PMC
Oxytocin has been revealed to work for anxiety suppression and anti-stress as well as for psychosocial behavior and reproductive functions. Oxytocin neurons are activated by various stressful stimuli. The oxytocin receptor is widely distributed ...
PsyPost
Oxytocin alters amygdala activation in response to angry faces ...
October 12, 2023 - A recent neuroimaging study has found that oxytocin administration decreases amygdala activity in individuals with antisocial personality disorder (ASPD), bringing it closer to the levels observed in healthy individuals. The findings suggest that oxytocin might have the potential to mitigate ...
ResearchGate
Oxytocin administration in the basolateral and central nuclei of ...
March 1, 2018 - Oxytocin (OT) at acting central nuclei decreases meal size and reduces intake of palatable sweet solutions. It remains largely unclear as to which brain sites mediate OT's effect on palatability versus energy or the combination of those aspects of consumption. Here, we expanded the search for sites that mediate anorexigenic properties of OT by focusing on two subdivisions of the amygdala...
Biomedcentral
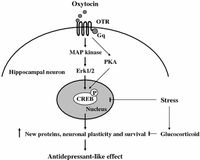
Oxytocin: a therapeutic target for mental disorders | The Journal ...
We review here that oxytocin (OT) is released into blood and within distinct brain regions in response to stressful and social stimuli, and has been shown to have an antidepressant-like effect in animal studies. Clinical reports suggest OT to be a promising drug for psychiatric diseases such ...
HealthCentral
Oxytocin: What It Is, How It Makes You Feel & Why It Matters
September 23, 2021 - If you’ve got questions about oxytocin—what it is, what it does, how it feels—you’ve come to the right place. We’re going to answer your many Qs right now, with help from top docs.